RNA-Seq Analysis of Differentiated Keratinocytes Reveals a Massive Response to Late Events during Human Papillomavirus 16 Infect

Model systems of human papillomavirus‐associated disease - Doorbar - 2016 - The Journal of Pathology - Wiley Online Library

Modulation of basal cell fate during productive and transforming HPV‐16 infection is mediated by progressive E6‐driven depletion of Notch - Kranjec - 2017 - The Journal of Pathology - Wiley Online Library

Organotypic raft cultures of early-passage wild-type HPV-16 cell lines... | Download Scientific Diagram

Dynamics of papillomavirus in vivo disease formation & susceptibility to high-level disinfection—Implications for transmission in clinical settings - eBioMedicine

Modulation of basal cell fate during productive and transforming HPV‐16 infection is mediated by progressive E6‐driven depletion of Notch - Kranjec - 2017 - The Journal of Pathology - Wiley Online Library

Modulation of basal cell fate during productive and transforming HPV‐16 infection is mediated by progressive E6‐driven depletion of Notch - Kranjec - 2017 - The Journal of Pathology - Wiley Online Library

E6AP is important for HPV E6's role in regulating epithelial homeostasis and its loss impairs keratinocyte commitment to differentiation | bioRxiv

Characterisation of the novel spontaneously immortalized and invasively growing human skin keratinocyte line HaSKpw | Scientific Reports

Role of E6 in Maintaining the Basal Cell Reservoir during Productive Papillomavirus Infection | Journal of Virology

Normal Growth and Differentiation in a Spontaneously Immortalized Near-Diploid Human Keratinocyte Cell Line, NIKS - ScienceDirect
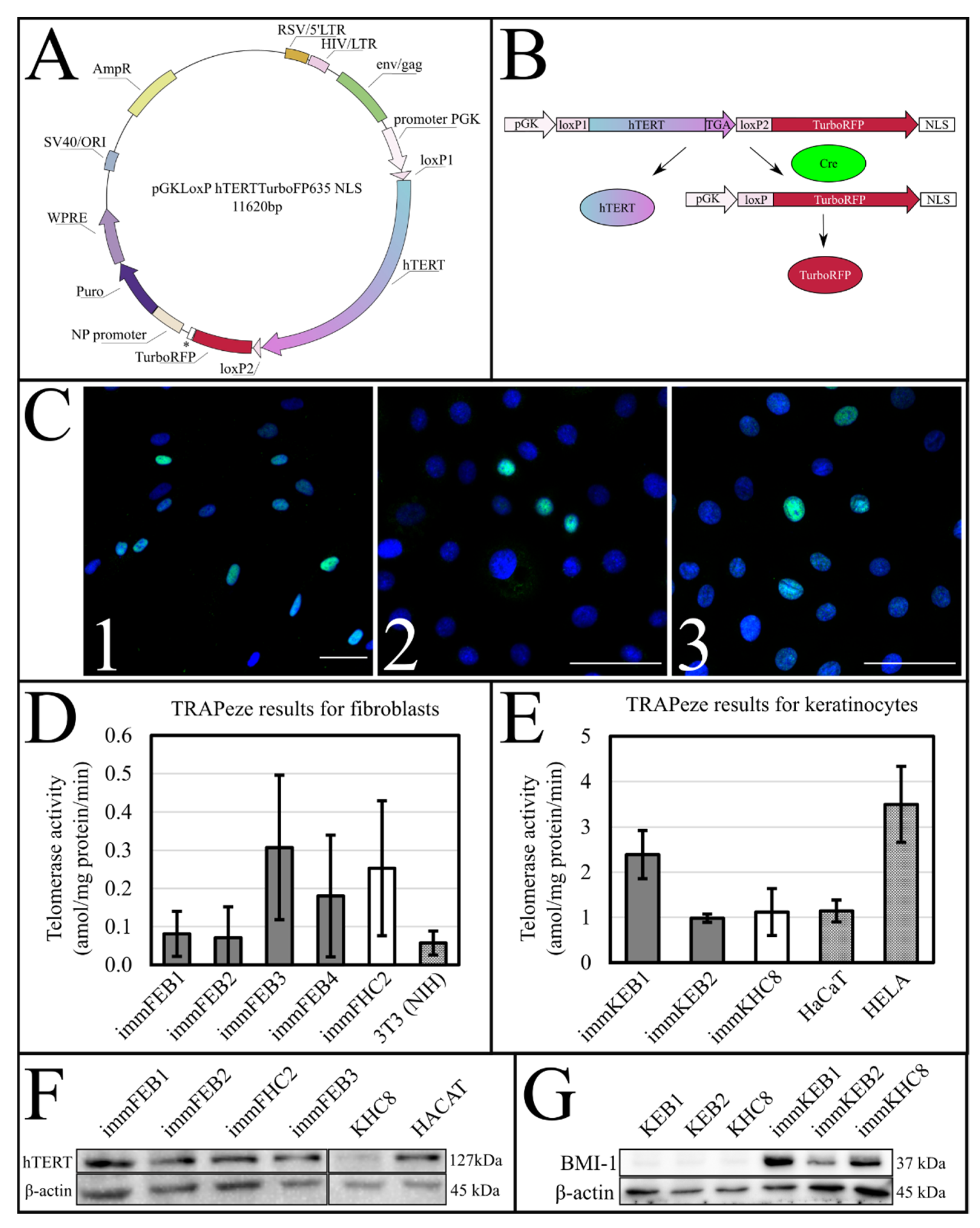
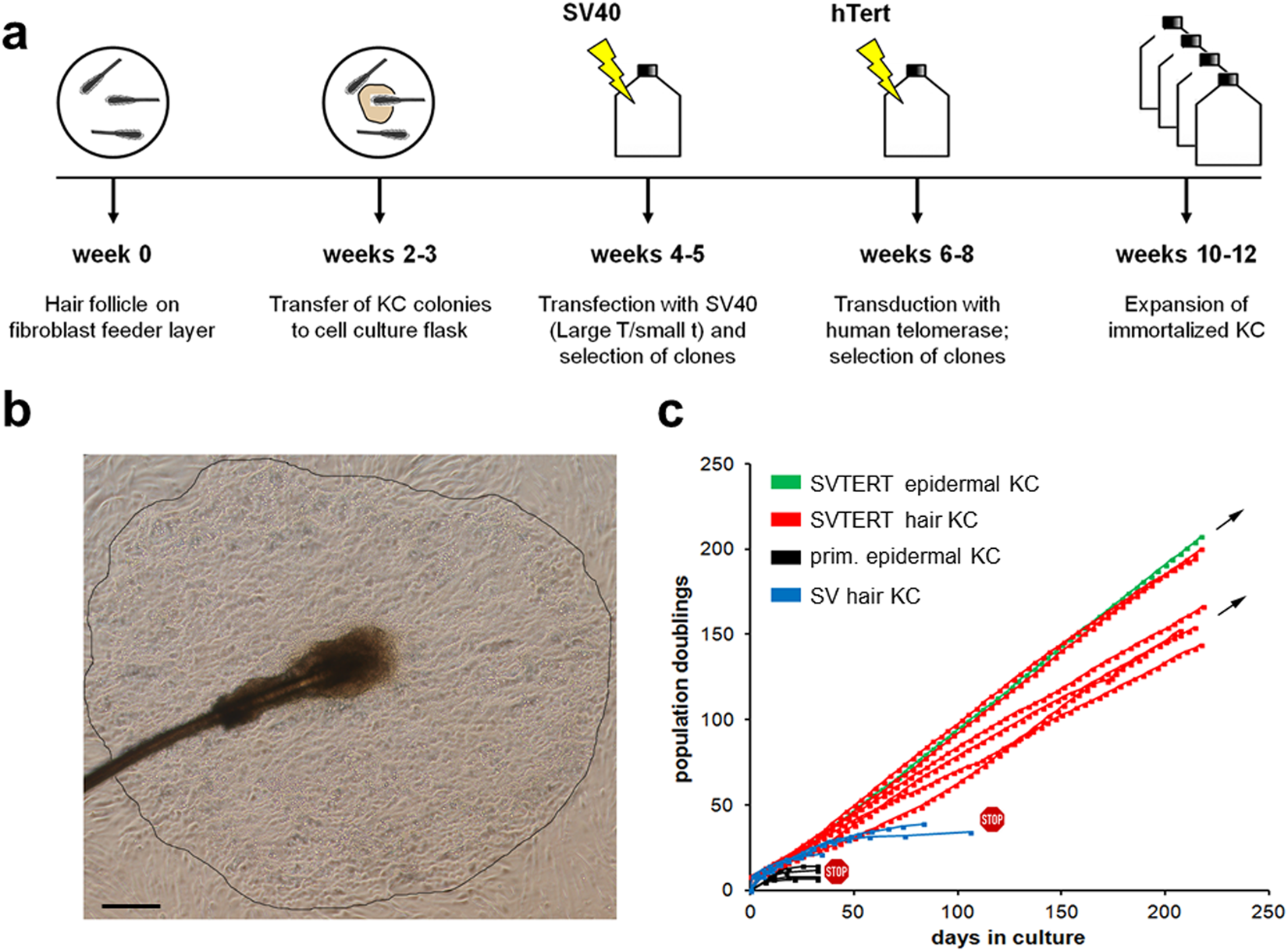
IJMS | Free Full-Text | hTERT-Driven Immortalization of RDEB Fibroblast and Keratinocyte Cell Lines Followed by Cre-Mediated Transgene Elimination
Human papillomaviruses sensitize cells to DNA damage induced apoptosis by targeting the innate immune sensor cGAS | PLOS Pathogens

E6AP is important for HPV E6's role in regulating epithelial homeostasis and its loss impairs keratinocyte commitment to differentiation | bioRxiv
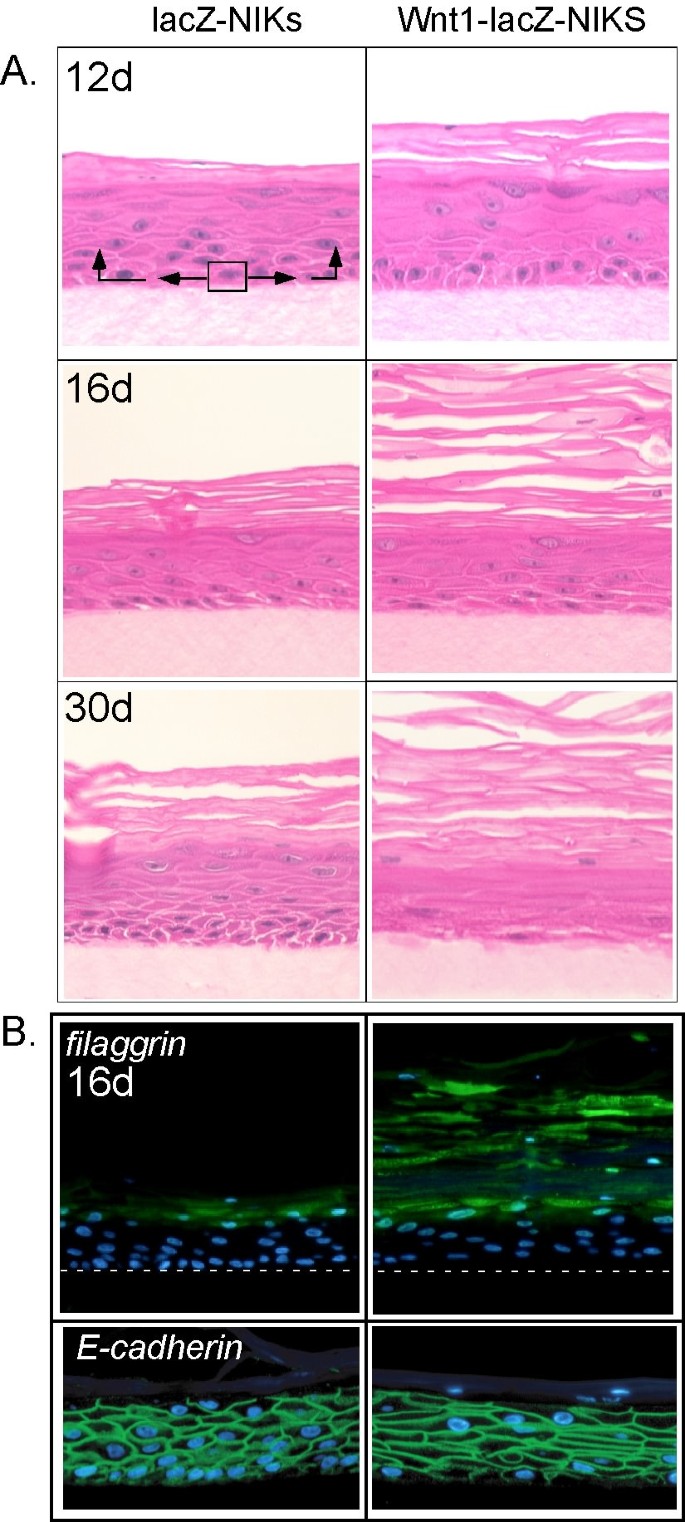
Wnt signaling induces differentiation of progenitor cells in organotypic keratinocyte cultures | BMC Developmental Biology | Full Text
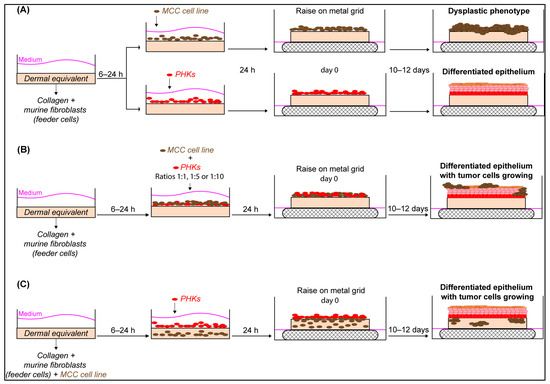
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Organotypic Epithelial Raft Cultures as a Three-Dimensional In Vitro Model of Merkel Cell Carcinoma

Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E1∧E4 Contributes to Multiple Facets of the Papillomavirus Life Cycle | Journal of Virology
Human papillomaviruses sensitize cells to DNA damage induced apoptosis by targeting the innate immune sensor cGAS | PLOS Pathogens
Roles for E1-independent replication and E6-mediated p53 degradation during low-risk and high-risk human papillomavirus genome maintenance | PLOS Pathogens
HPV16 and 18 genome amplification show different E4-dependence, with 16E4 enhancing E1 nuclear accumulation and replicative efficiency via its cell cycle arrest and kinase activation functions | PLOS Pathogens

Reconstruction of human papillomavirus type 16-mediated early-stage neoplasia implicates E6/E7 deregulation and the loss of contact inhibition in neoplastic progression. - Abstract - Europe PMC